[最も人気のある!] coupon bond yield to maturity formula 126500-Yield to maturity for coupon bond formula semi annual
Calculation of the Coupon Bond (Step by Step) The formula for coupon bond calculation can be done by using the following steps Step 1 Firstly, determine the par value of the bond issuance, and it is denoted by PP = Bond Price;There are two ways of looking at bond yields current yield and yield to maturity Current Yield This is is the annual return earned on the price paid for a bond It is calculated by dividing the bond's coupon rate by its purchase price For example, let's say a bond has a coupon rate of 6% on a face value of Rs 1,000 The interest earned
How To Calculate Bond Price In Excel
Yield to maturity for coupon bond formula semi annual
Yield to maturity for coupon bond formula semi annual-Coupon vs Yield to Maturity A bond has a variety of features when it's first issued, including the size of the issue, the maturity date, and the initial couponFor example, the US Treasury might issue a 30year bond in 19 that's due in 49 with a coupon of 2%N = No of periods till maturity;



Yields To Maturity On Zero Coupon Ronds Bond Math
The coupon rate Coupon Rate A coupon rate is the amount of annual interest income paid to a bondholder, based on the face value of the bond for the bond is 15% and the bond will reach maturity in 7 years The formula for determining approximate YTM would look like below The approximated YTM on the bond is 1853% Importance of Yield to MaturityFormula for Calculating the Effective Yield The formula for calculating the effective yield on a bond purchased Effective Yield = 1 (i/n) n – 1 Where i – The nominal interest rate on the bond;Formula for yield to maturity Yield to maturity(YTM) = (Face value/Bond price) 1/Time period1 As can be seen from the formula, the yield to maturity and bond price are inversely correlated Consider a 30year, zerocoupon bond with a face value of $100
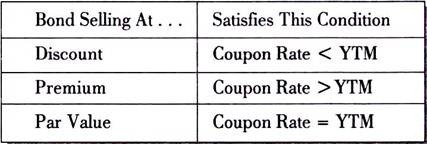
Bond YieldtoMaturity Imagine you are interested in buying a bond, at a market price that's different from the bond's par value One thing to notice is that the YTM is greater than the current yield, which in turn is greater than the coupon rate (Current yield is $70/$950 = 737%) This will always be true for a bond selling at a discountThe yield to maturity formula is a more complicated calculation that renders the total amount of return generated by a bond based on its par value, purchase price, duration, coupon rate, and the power of compound interest This calculation is useful for investors looking to maximize profits by holding a bond until maturity, because it includes the interest that could be earned if annual couponC = the semiannual coupon interest;
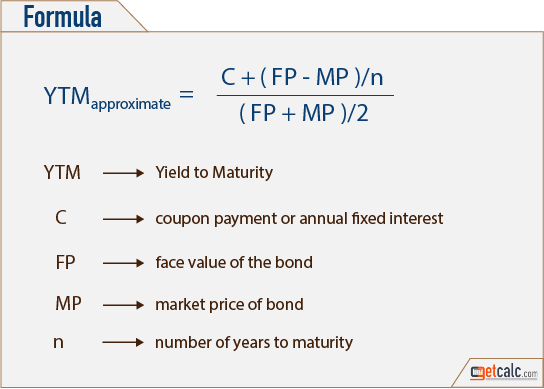
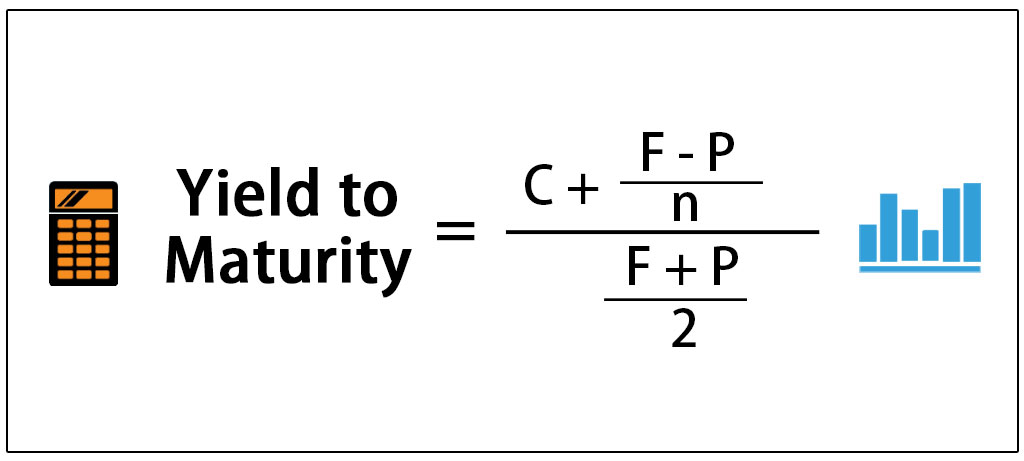
The yield to maturity formula is a more complicated calculation that renders the total amount of return generated by a bond based on its par value, purchase price, duration, coupon rate, and the power of compound interest This calculation is useful for investors looking to maximize profits by holding a bond until maturity, because it includes the interest that could be earned if annual couponIt's difficult to calculate the exact YTM, but in the formulas below we'll look at how you can calculate the approximate yield to maturity of a bond Yield to Maturity Formula YTM = \dfrac{ C \dfrac{FP}{n} }{ \dfrac{FP}{2}} C = Coupon/interest payment;Yield to maturity (YTM) is the annual return that a bond is expected to generate if it is held till its maturity given its coupon rate, payment frequency and current market price Yield to maturity is essentially the internal rate of return of a bond ie the discount rate at which the present value of a bond's coupon payments and maturity value is equal to its current market price


Bond Yield To Maturity Ytm Calculator


Http People Stern Nyu Edu Jcarpen0 Courses B 03yield Pdf
The difference between the current price of the bond, ie, $, and its Face Value, ie, $1000, is the amount of compound interest that will be earned over the 10year life of the Bond Thus Cube Bank will pay $ and will receive $1000 at the end of 10 years, ie, on the maturity of the Zero Coupon Bond, thereby earning an effective yield of 8%F = Face value;N = number of semiannual periods left to maturity;


Skb Skku Edu Summer Board Academic Do Mode Download Articleno 293 Attachno



Modified Duration
Yield to Maturity Calculator is an online tool for investment calculation, programmed to calculate the expected investment return of a bond This calculator generates the output value of YTM in percentage according to the input values of YTM to select the bonds to invest in, Bond face value, Bond price, Coupon rate and years to maturityCalculation of Convexity Example For a Bond of Face Value USD1,000 with a semiannual coupon of 80% and a yield of 10% and 6 years to maturity and a present price of , the duration is 4 years, the modified duration is 459, and the calculation for Convexity would beThe current yield differs from the yield to maturity in that the yield to maturity looks at all future inflows, including a higher or lower face value than its current price, to determine the yield based on a present value equal to the current price of the bond The formula for current yield only looks at the current price and one year coupons



Coupon Rate Vs Yield Rate For Bonds Wall Street Oasis


Yield To Maturity Ytm Definition Formula Method Example Approximation Excel
Yield to Maturity (YTM) Overview, Formula, and Importance CODES (2 days ago) The coupon rate Coupon Rate A coupon rate is the amount of annual interest income paid to a bondholder, based on the face value of the bond for the bond is 15% and the bond will reach maturity in 7 years The formula for determining approximate YTM would look like below The approximated YTM on the bond is 1853%The current yield differs from the yield to maturity in that the yield to maturity looks at all future inflows, including a higher or lower face value than its current price, to determine the yield based on a present value equal to the current price of the bond The formula for current yield only looks at the current price and one year couponsBond pricing formula depends on factors such as a coupon, yield to maturity, par value and tenor These factors are used to calculate the price of the bond in the primary market In the secondary market, other factors come into play such as creditworthiness of issuing firm, liquidity and time for next coupon payments



Yields To Maturity On Zero Coupon Ronds Bond Math


Yield To Maturity Definition How To Calculate Ytm Pros Cons
Coupon on the bond will be $1,000 * 850% / 2 which is $425, since this pays semiannually Yield to Maturity (Approx) = (4250 (1000 – 9) / (10 * 2))/ ( ( 1000 9 )/2) Yield to Maturity will be –N – The number of coupon payments received in each year Practical Example Assume that you purchase a bond with a nominal coupon rate of 7%The yield to maturity formula is a more complicated calculation that renders the total amount of return generated by a bond based on its par value, purchase price, duration, coupon rate, and the power of compound interest This calculation is useful for investors looking to maximize profits by holding a bond until maturity, because it includes the interest that could be earned if annual coupon


Calculating The Yield To Maturity Ytm Of A Bond Financial Management
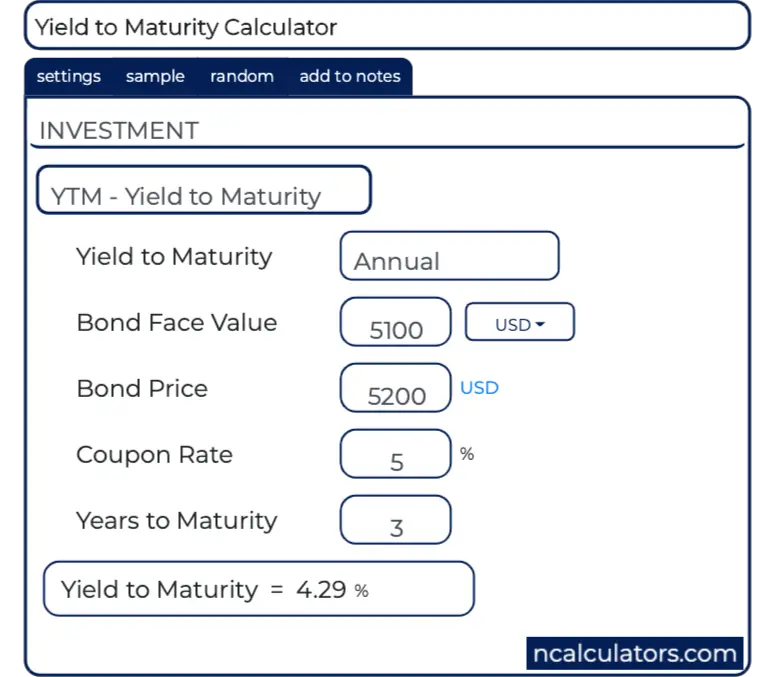


Yield To Maturity Ytm Calculator
Definition The yield to maturity (YTM) of a bond is the internal rate of return (IRR) if the bond is held until the maturity date In other words, YTM can be defined as the discount rate at which the present value of all coupon payments and face value is equal to the current market price of a bondSpot Interest Rate vs Yield to Maturity Yield to maturity and spot interest rate in case of purediscount bonds ie zerocoupon bonds are the same However, in case of couponpaying bonds, yield to maturity is the (somewhat) weighted average of the individual spot interest rates that apply to each cash flow of the bondYou can keep Coupon Bond Yield To Maturity Formula listening with unlimited skips and listen to all their favorite music offline Starts at $799/month after the promotional period This promotional offer is valid for new Coupon Bond Yield To Maturity Formula subscribers



Zero Coupon Bond Definition Formula Examples Calculations
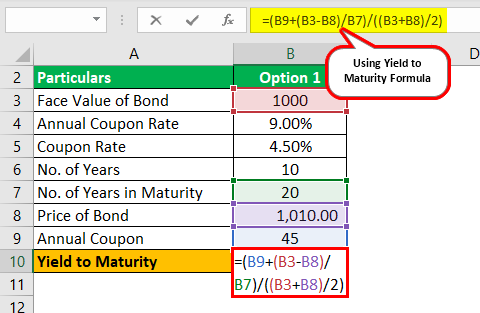


Yield To Maturity Formula Step By Step Calculation With Examples
Formula to Calculate Bond Price The formula for bond pricing is basically the calculation of the present value of the probable future cash flows, which comprises of the coupon payments and the par value, which is the redemption amount on maturity The rate of interest which is used to discount the future cash flows is known as the yield to maturity (YTM)P is the price of a bond, C is the periodic coupon payment, r is the yield to maturity (YTM) of a bond, B is the par value or face value of a bond, Y is the number of years to maturity Example 2 Suppose a bond is selling for $980, and has an annual coupon rate of 6% It matures in five years, and the face value is $1000 What is the Yield toN = number of semiannual periods left to maturity;
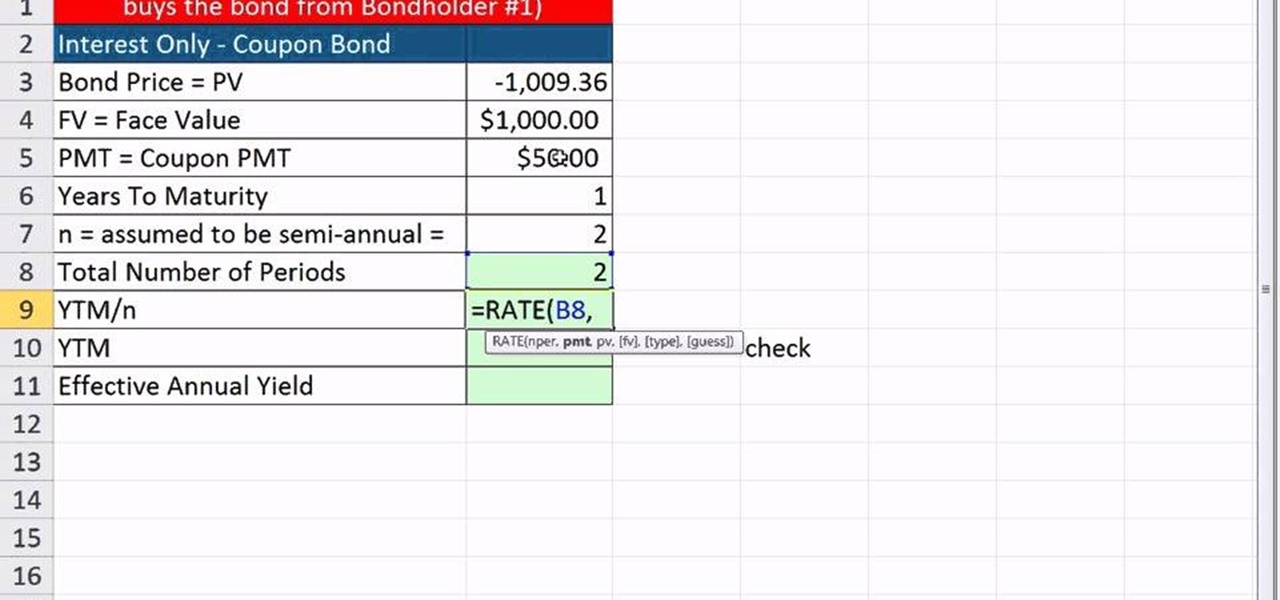


How To Calculate Ytm And Effective Annual Yield From Bond Cash Flows In Excel Microsoft Office Wonderhowto
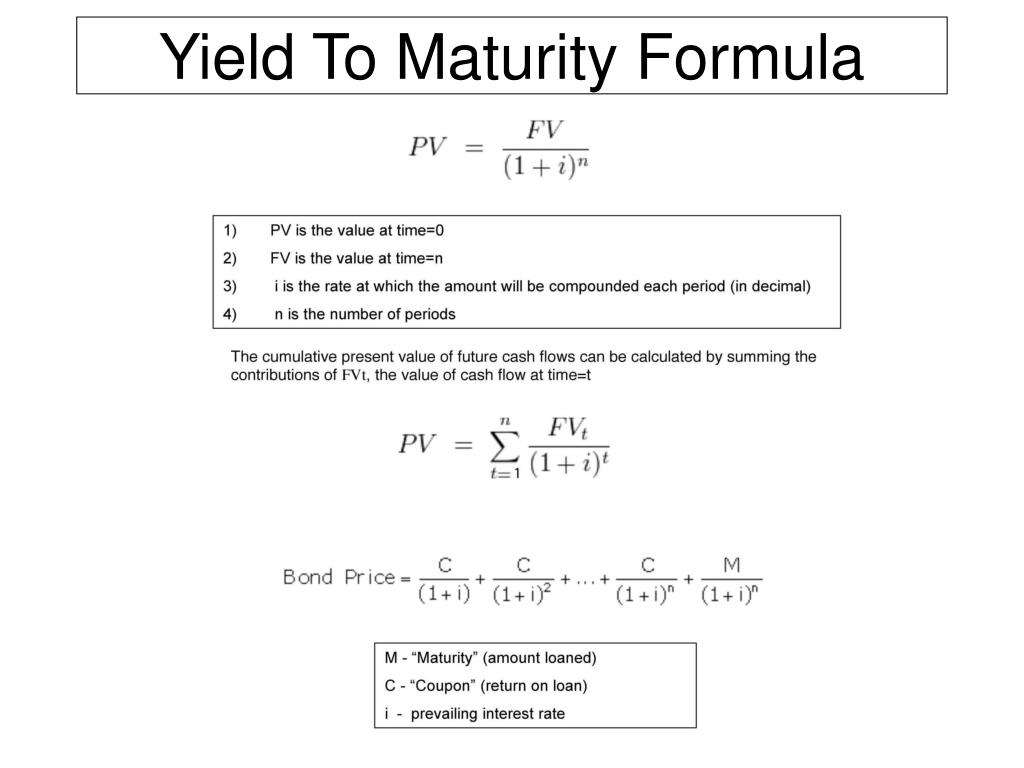


Ppt Yield To Maturity Formula Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
The yield to maturity (YTM) is the percentage rate of return for a bond assuming that the investor holds the asset until its maturity date It is the sum of all of its remaining coupon payments ALet's take an example to understand how to use the formula Let us find the yieldtomaturity of a 5 year 6% coupon bond that is currently priced at $850 The calculation of YTM is shown belowEnter the bond's trading price, face or par value, time to maturity, and coupon or stated interest rate to compute a current yield The tool will also compute yield to maturity, but see the YTM calculator for a better explanation plus the yield to maturity formula Bond Yield Calculator
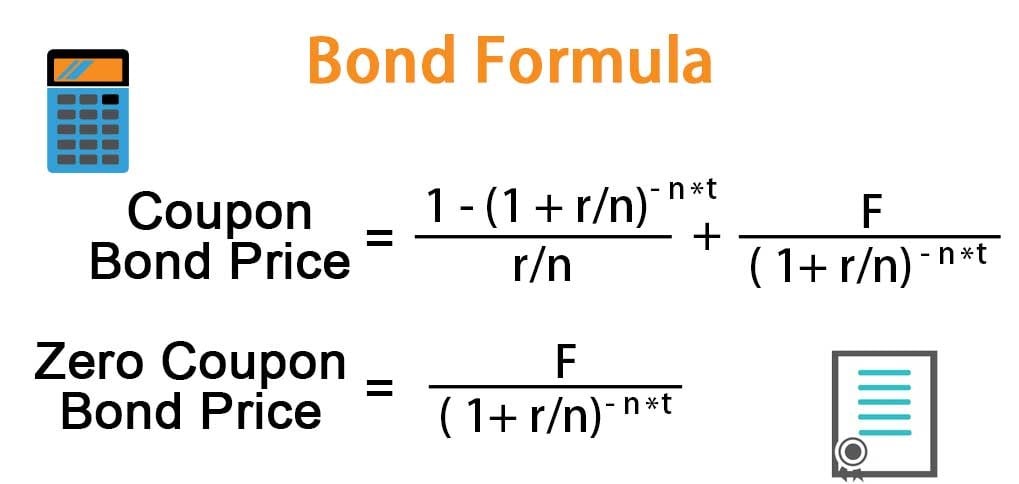


Bond Formula How To Calculate A Bond Examples With Excel Template



How To Calculate Yield To Maturity 9 Steps With Pictures
P = Bond Price;The yield to maturity (YTM), book yield or redemption yield of a bond or other fixedinterest security, such as gilts, is the (theoretical) internal rate of return (IRR, overall interest rate) earned by an investor who buys the bond today at the market price, assuming that the bond is held until maturity, and that all coupon and principal payments are made on scheduleCoupon vs Yield to Maturity A bond has a variety of features when it's first issued, including the size of the issue, the maturity date, and the initial couponFor example, the US Treasury might issue a 30year bond in 19 that's due in 49 with a coupon of 2%
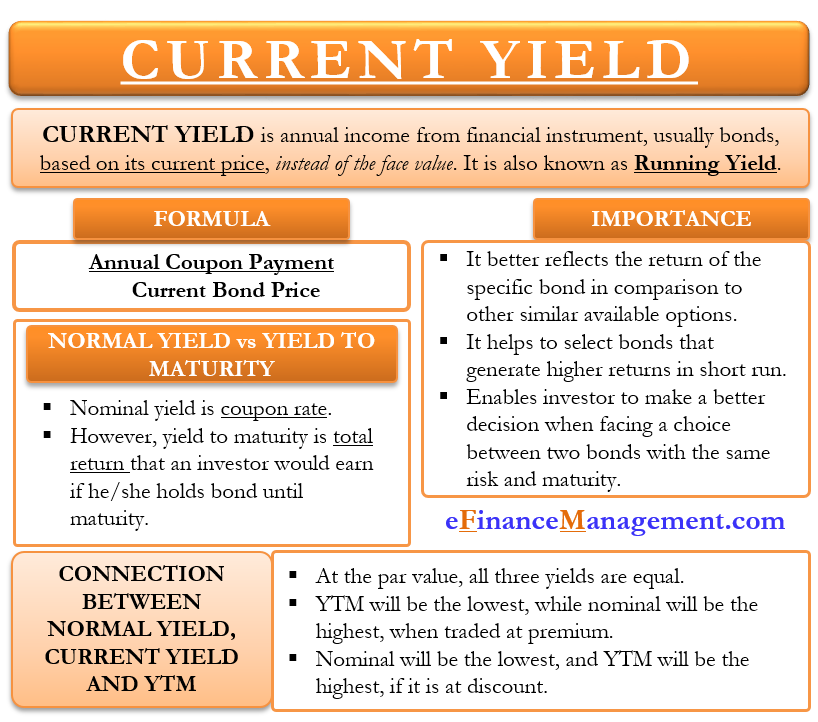


Current Yield Meaning Importance Formula And More
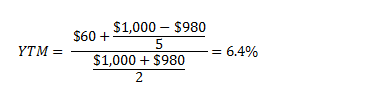


What Is The Difference Between Irr And The Yield To Maturity The Motley Fool
A bond that sells at a premium (where price is above par value) will have a yield to maturity that is lower than the coupon rate Alternatively, the causality of the relationship between yield to maturity Cost of Debt The cost of debt is the return that a company provides to its debtholders and creditorsN = Years to maturityExample of Yield to Maturity Formula The price of a bond is $9 with a face value of $1000 which is the face value of many bonds Assume that the annual coupons are $100, which is a 10% coupon rate, and that there are 10 years remaining until maturity This example using the approximate formula would be
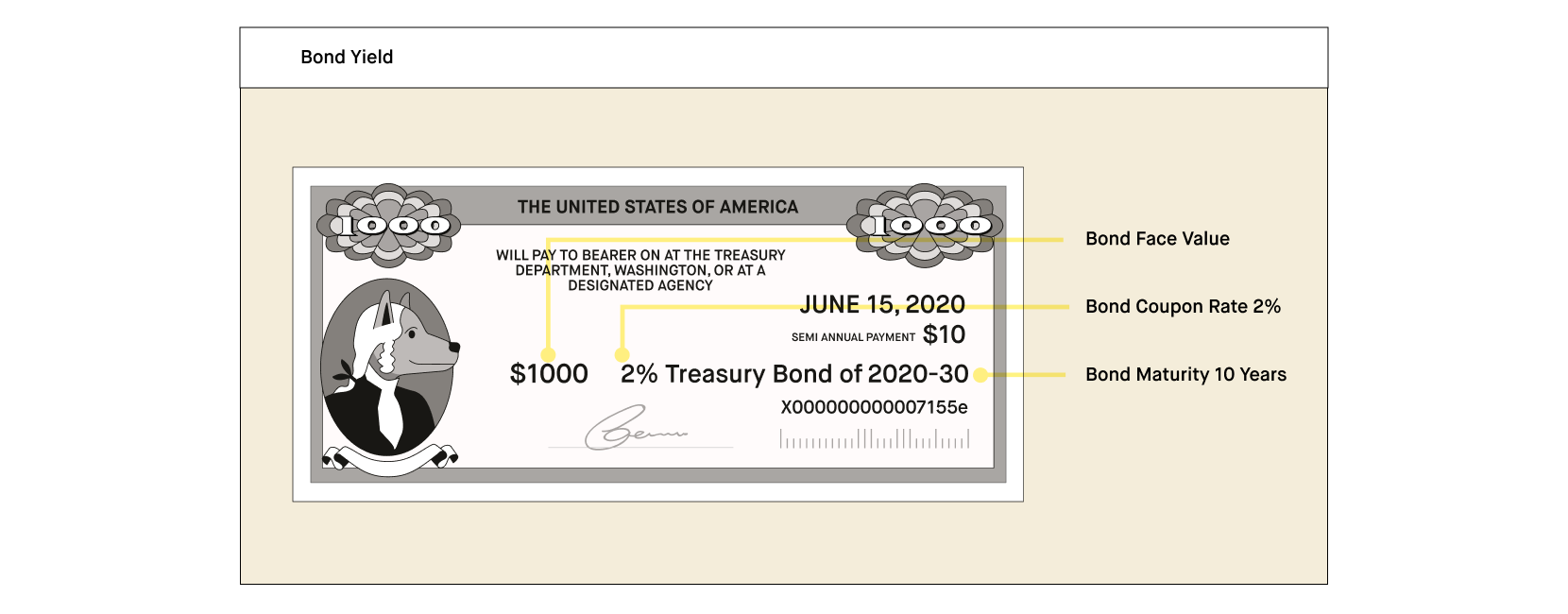


What Is A Bond Yield Robinhood



Youtube Bond Maturity
P = Par value of bond, YTM = Yield to maturity;Enter the bond's trading price, face or par value, time to maturity, and coupon or stated interest rate to compute a current yield The tool will also compute yield to maturity, but see the YTM calculator for a better explanation plus the yield to maturity formula Bond Yield CalculatorC = the semiannual coupon interest;



Zero Coupon Bonds Invest In Zero Coupon Bonds Today
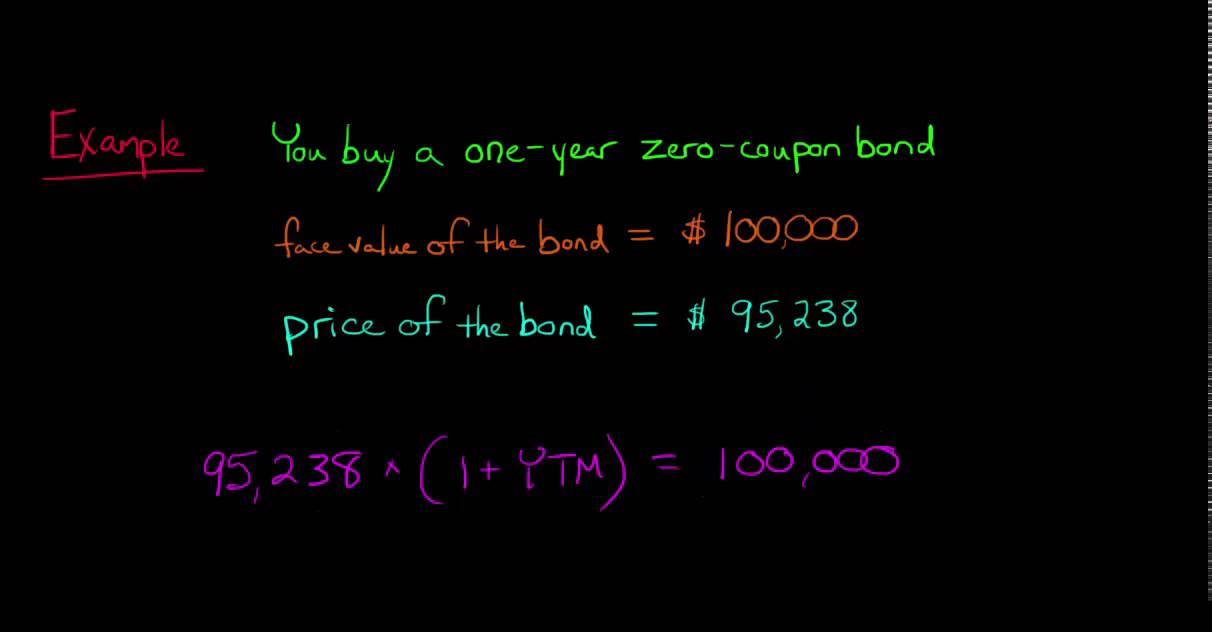


Calculating The Yield Of A Zero Coupon Bond Youtube
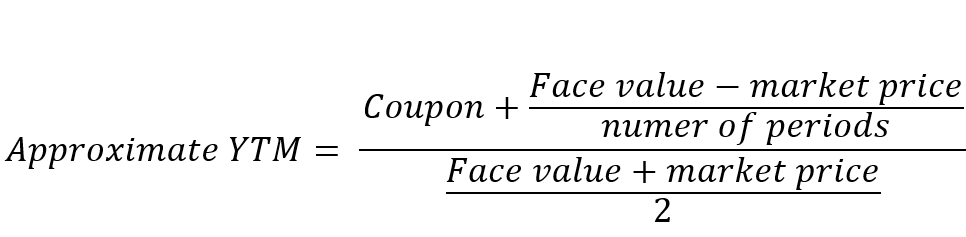
Current yield, by definition, is the annual rate of return that you receive for the price paid for that bond The formula of current yield Coupon rate / Purchase price Naturally, if the bond purchase price is equal to the face value, current yield will be equal to the coupon rate Current Yield= 160/2,000 = 008 or 8%Understanding a bond's yield to maturity (YTM) is an essential task for fixed income investors But to fully grasp YTM, we must first discuss how to price bonds in general The price of aThe formula for the approximate yield to maturity on a bond is ( (Annual Interest Payment) ( (Face Value Current Price) / (Years to Maturity) ) ) ( ( Face Value Current Price ) / 2 )



Zero Coupon Bond Yield Calculator Ytm Of A Discount Bond



Berk Chapter 8 Valuing Bonds
Let's take an example to understand how to use the formula Let us find the yieldtomaturity of a 5 year 6% coupon bond that is currently priced at $850 The calculation of YTM is shown belowFormula to Calculate Bond Price The formula for bond pricing is basically the calculation of the present value of the probable future cash flows, which comprises of the coupon payments and the par value, which is the redemption amount on maturity The rate of interest which is used to discount the future cash flows is known as the yield to maturity (YTM)The formula for Bond Yield can be calculated by using the following steps Step 1 Firstly, determine the bond's par value be received at maturity and then determine coupon payments to be received periodically Both par value and periodic coupon payments constitute the potential future cash flows Step 2
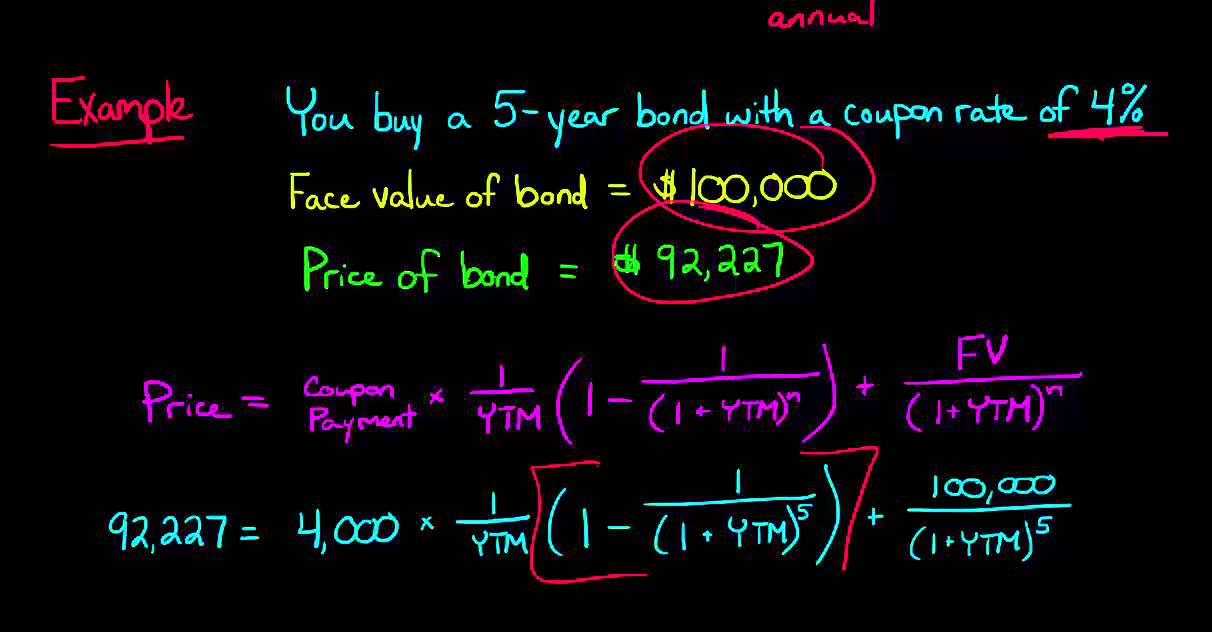


Calculating The Yield Of A Coupon Bond Using Excel Youtube



Quant Bonds Between Coupon Dates
Yield to Maturity Calculator is an online tool for investment calculation, programmed to calculate the expected investment return of a bond This calculator generates the output value of YTM in percentage according to the input values of YTM to select the bonds to invest in, Bond face value, Bond price, Coupon rate and years to maturityYield To Maturity Of Zero Coupon Bond CODES (11 days ago) Zero Coupon Bond Yield Formula (with Calculator) CODES (2 days ago) A zero coupon bond is a bond that does not pay dividends (coupons) per period, but instead is sold at a discount from the face value For example, an investor purchases one of these bonds at $500, which has a faceSpot Interest Rate vs Yield to Maturity Yield to maturity and spot interest rate in case of purediscount bonds ie zerocoupon bonds are the same However, in case of couponpaying bonds, yield to maturity is the (somewhat) weighted average of the individual spot interest rates that apply to each cash flow of the bond



How To Calculate Bond Price In Excel


Q Tbn And9gcs8pllmjk Cwco2cxddqmohomgedhyw Veiacyoq Lypi38bu2o Usqp Cau
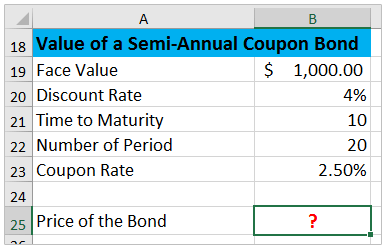
Nper = Total number of periods of the bond maturity Years to maturity of the bond is 5 years But coupons per year is 2 So, nper is 5 x 2 = 10 Pmt = The payment made in every period It cannot change over the life of the bond The coupon rate is 6% But as payment is done twice a year, the coupon rate for a period will be 6%/2 = 3%The difference between the current price of the bond, ie, $, and its Face Value, ie, $1000, is the amount of compound interest that will be earned over the 10year life of the Bond Thus Cube Bank will pay $ and will receive $1000 at the end of 10 years, ie, on the maturity of the Zero Coupon Bond, thereby earning an effective yield of 8%Nominal yield, or the coupon rate, is the stated interest rate of the bond This yield percentage is the percentage of par value —$5,000 for municipal bonds, and $1,000 for most other bonds — that is usually paid semiannually Thus, a bond with a $1,000 par value that pays 5% interest pays $50 dollars per year in 2 semiannual payments of $25
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Current_Yield_vs_Yield_to_Maturity_Nov_2020-01-c4613a2a2029466a960d9e3594841a03.jpg)


Current Yield Vs Yield To Maturity



Yield To Maturity Fixed Income
While the current yield and yieldtomaturity (YTM) formulas both may be used to calculate the yield of a bond, each method has a different application—depending on an investor's specific goals



21 Cfa Level I Exam Cfa Study Preparation


Calculating Yield To Maturity Using The Bond Price



Vba To Calculate Yield To Maturity Of A Bond
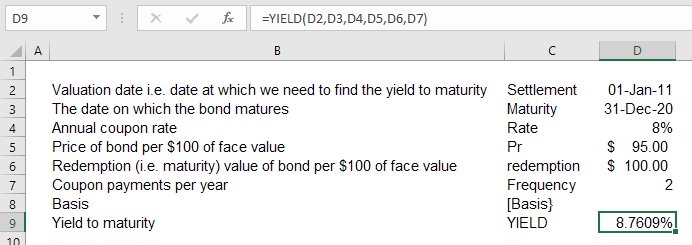


Yield To Maturity Ytm Definition Formula And Example
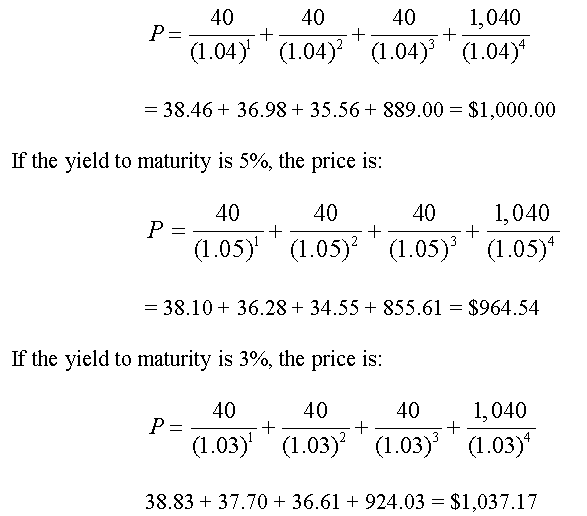


An Introduction To Bonds Bond Valuation Bond Pricing


The Dummies Guide To Zero Coupon Bonds



Yield Curve Wikipedia
%201.jpg)


Bond Valuation



Bonds Bond Prices Interest Rates And Holding Period Return Ppt Download


Microsoft Excel Bond Yield Calculations Tvmcalcs Com



Bond Pricing And Accrued Interest Illustrated With Examples
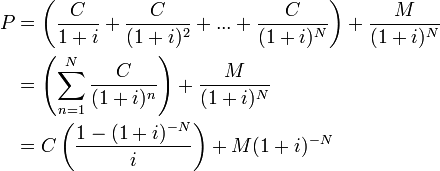


Valuing Bonds Boundless Finance
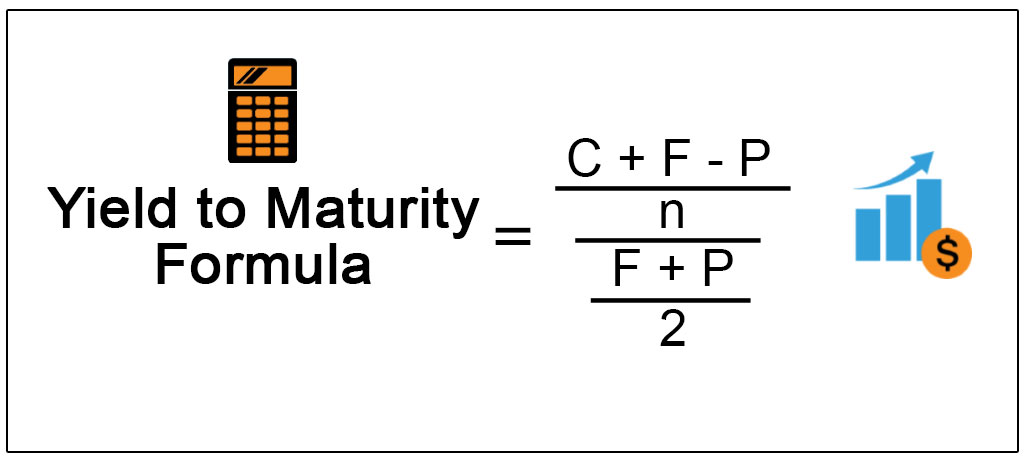


Yield To Maturity Formula Step By Step Calculation With Examples
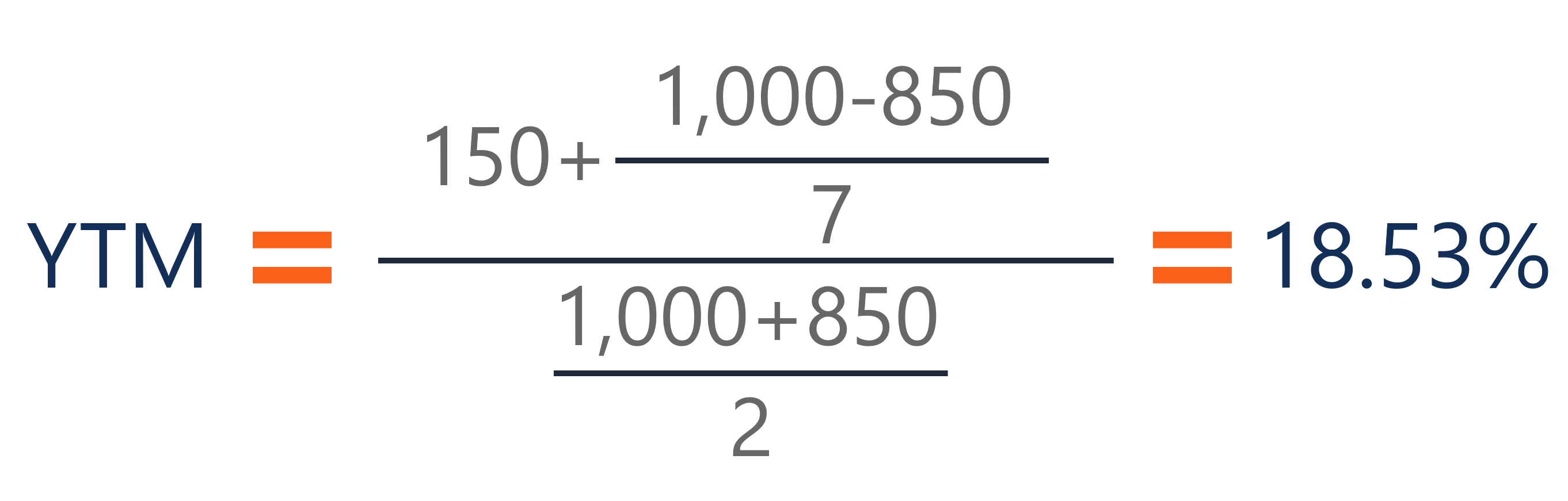


Yield To Maturity Ytm Overview Formula And Importance
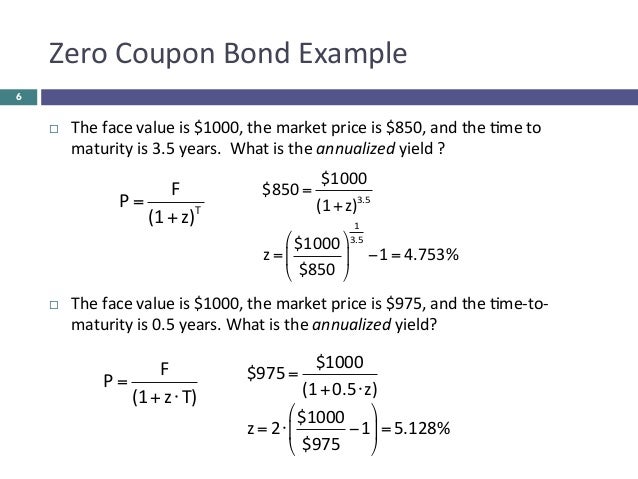


Bond Yield To Maturity Ytm Calculator



Chapter 4 Solutions



Berk Chapter 8 Valuing Bonds
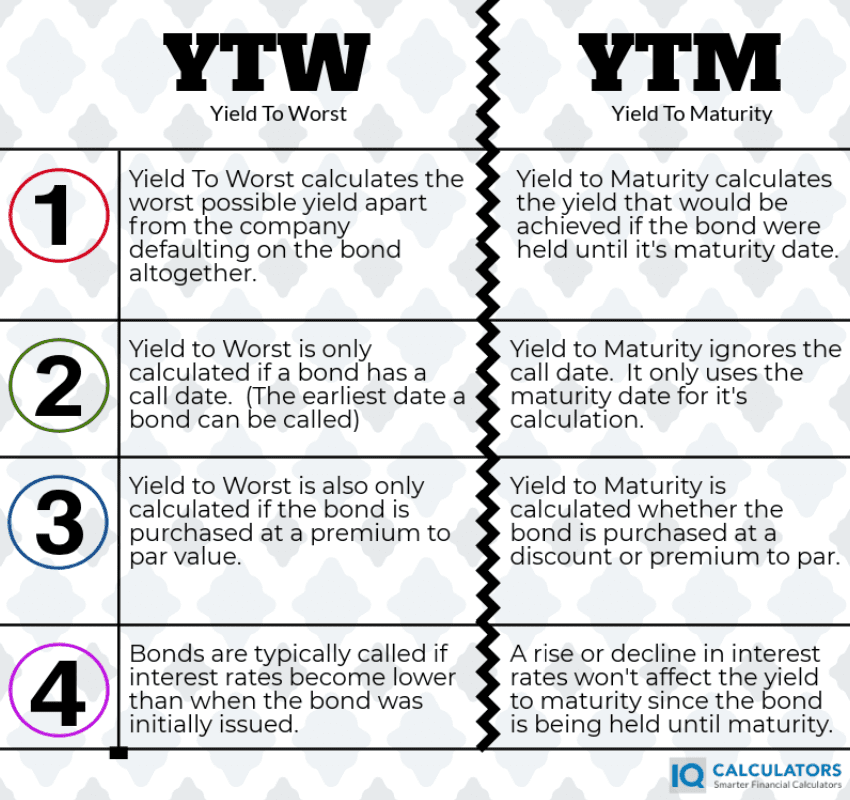


Yield To Worst What It Is And Why It S Important


Q Tbn And9gct1q6zxynbcvmgspi Wpg Zzjvgvz 1ltnjyviqmbaypurzxz Usqp Cau
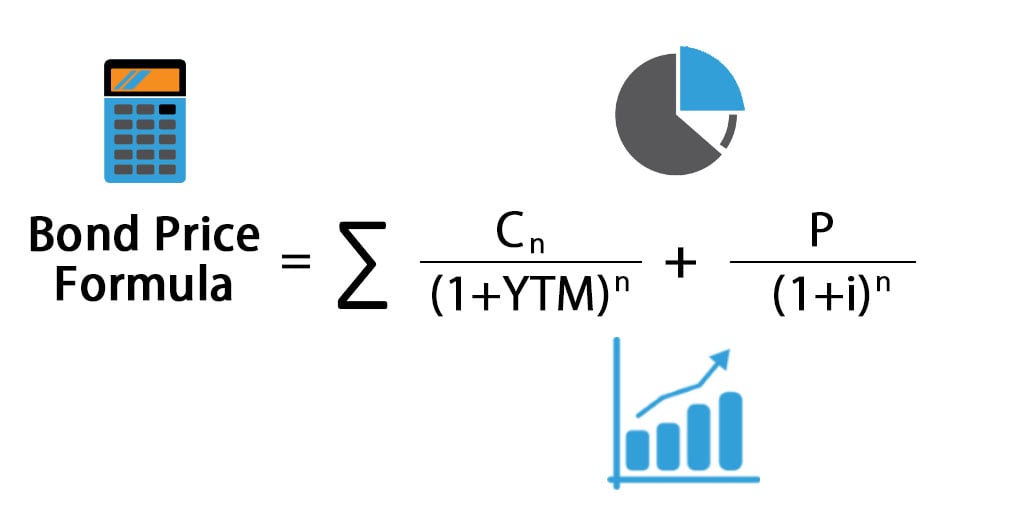


Bond Pricing Formula How To Calculate Bond Price



How To Calculate Yield To Maturity Definition Equation Example Financial Accounting Class Video Study Com
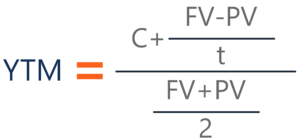


Yield To Maturity Ytm Overview Formula And Importance



Corporate Finance Berk Demarzo
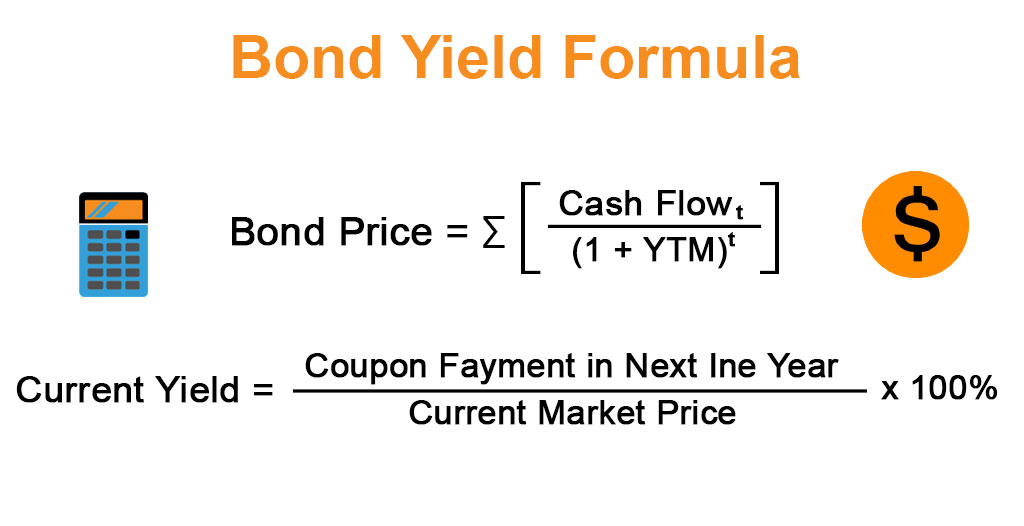


Bond Yield Formula Calculator Example With Excel Template



Chapter 6 Bonds 6 1 Chapter Outline 6 1 Bond Terminology 6 2 Zero Coupon Bonds 6 3 Coupon Bonds 6 4 Why Bond Prices Change 6 5 Corporate Bonds Ppt Download



What Is Coupon Rate In Bonds Know More Fincash Com


Zero Coupon Bond



Calculating The Yield To Maturity Mastering Python For Finance Second Edition



What Is A Zero Coupon Bond
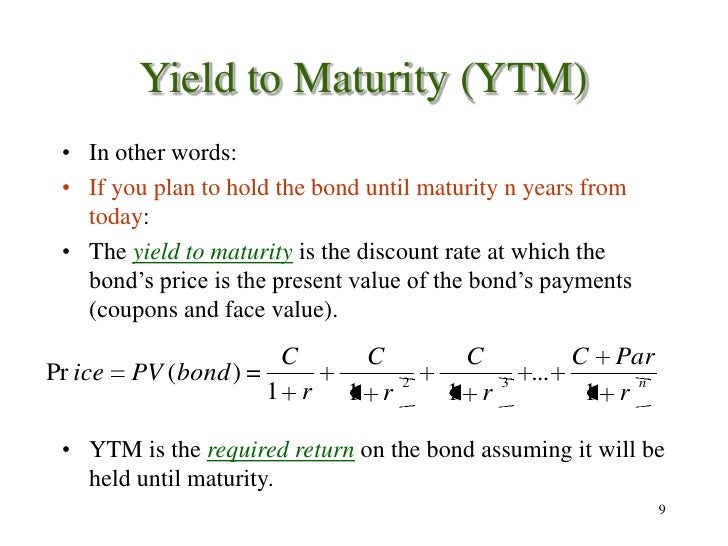


Ch7
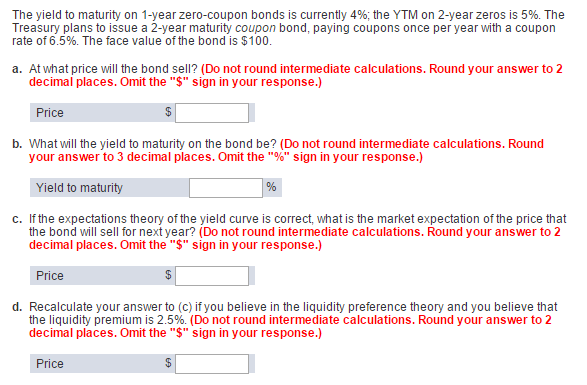


Solved The Yield To Maturity On 1 Year Zero Coupon Bonds Chegg Com



Solved Write Down The Formula That Is Used To Calculate T Chegg Com


What Is The Yield To Maturity Ytm Of A Zero Coupon Bond With A Face Value Of 1 000 Current Price Of 0 And Maturity Of 4 0 Years Recall That The Compounding Interval



How To Use The Excel Yield Function Exceljet


Http Kevinx Chiu Weebly Com Uploads 8 9 8 3 380 Homework 3 Solutions Pdf



Chapter 10 Bond Prices And Yields Pdf Free Download


Microsoft Excel Bond Yield Calculations Tvmcalcs Com
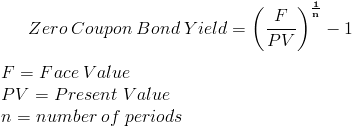


Zero Coupon Bond Yield Formula With Calculator
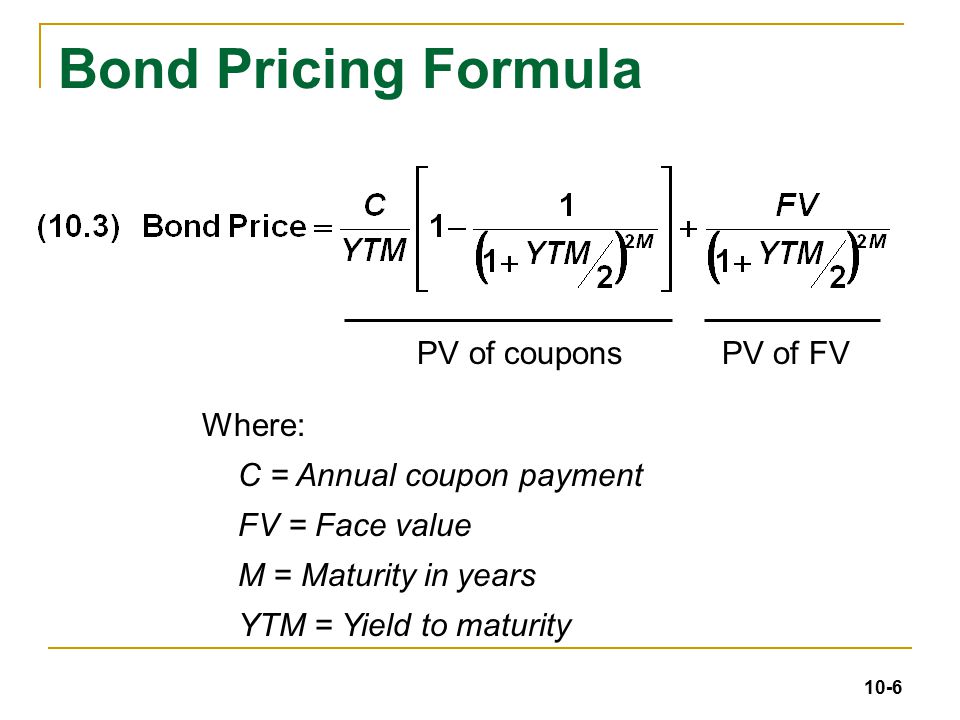


Chapter 10 Bond Prices And Yields 4 19 Ppt Download



What Is Yield To Maturity How To Calculate It Scripbox


Stata Codes For Calculating Yield To Maturity For Coupon Bonds Stataprofessor


1



Bonds Yields And Yield To Maturity Economics Online
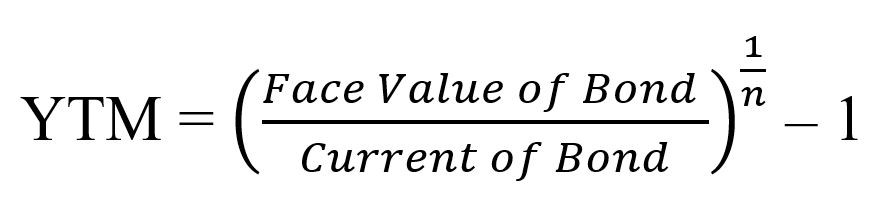


What You Must Know On Bond Valuation And Yield To Maturity Acca Afm Got It Pass
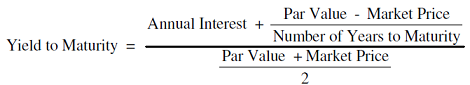


What Is Yield And How Does It Differ From Coupon Rate


Bond Yield To Maturity Calculator For Comparing Bonds



Bond Basics Bond Yields Flashcards Quizlet
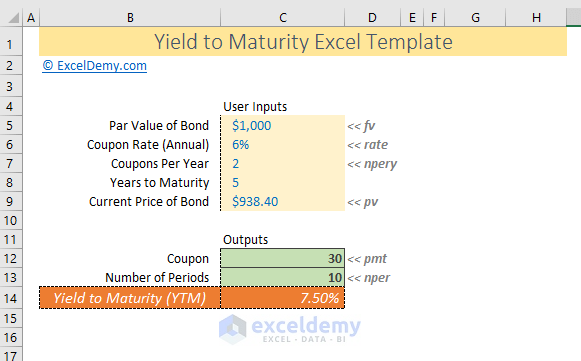


How To Calculate Yield To Maturity In Excel With Template Exceldemy



Price Of Bonds Corporate Financial Management
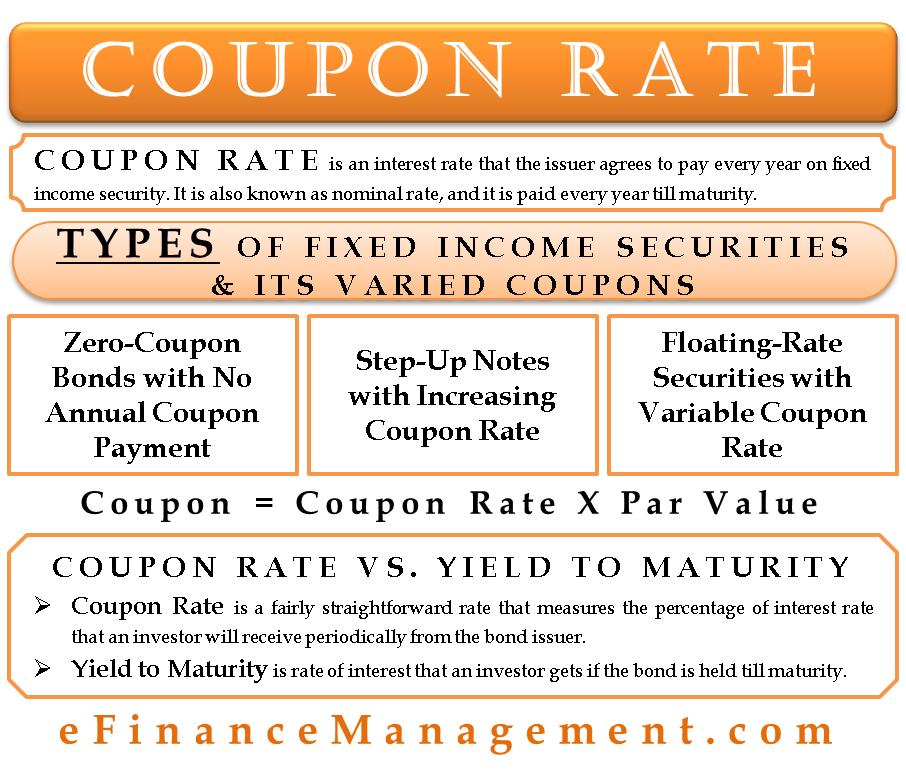


Coupon Rate Meaning Example Types Yield To Maturity Comparision


Www Jstor Org Stable



Calculate The Ytm Of A Coupon Bond Youtube


How To Calculate Bond Prices And Yields On The Series 7 Exam Dummies



Workshop 8 Answers Finance 261 Fin261 Studocu



How To Calculate Yield To Maturity 9 Steps With Pictures
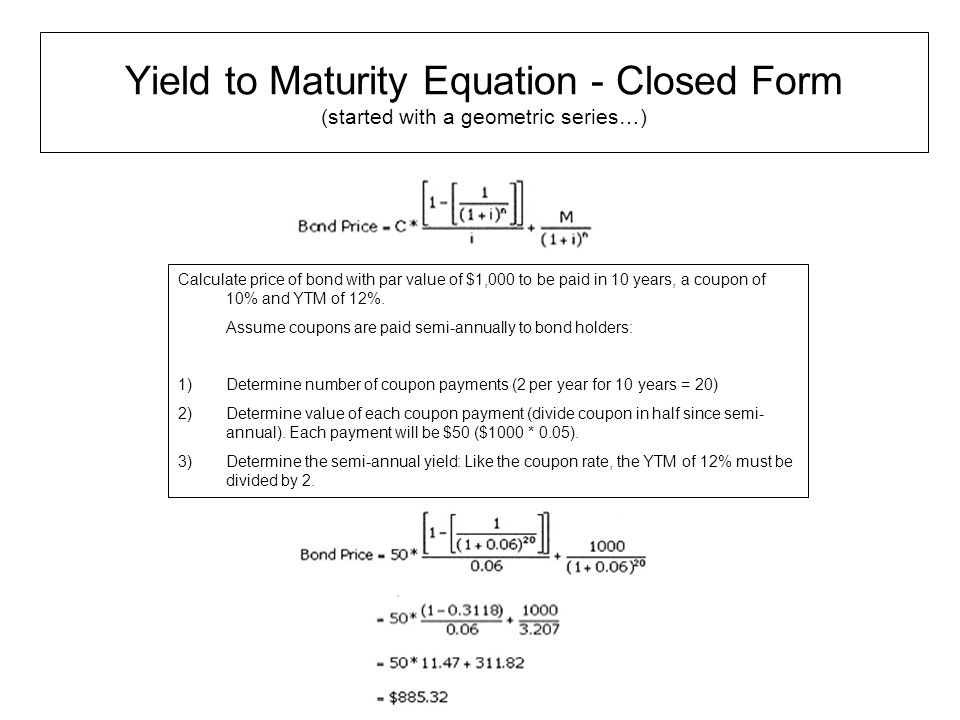


Yield To Maturity Formula Ppt Download


Q Tbn And9gcspuy9giugvfcvueflrzidtvhlsn9e5eqcnannn Rbj6l5qub Usqp Cau



Bond Yield To Call Ytc Calculator



Bonds Yield To Worst Current Yield Vs Yield To Maturity


Learn To Calculate Yield To Maturity In Ms Excel



What Is Yield To Maturity How To Calculate It Scripbox



Ytm Formula Excel
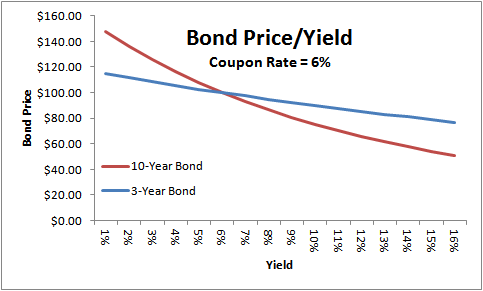


Bond Yields Nominal And Current Yield Yield To Maturity Ytm With Formulas And Examples



Yield To Maturity Ytm And Yield To Call Ytc alectures Com
/dotdash_Final_Yield_to_Worst_YTW_Oct_2020-01-cabc0d0cf5b64ef0b4f72afb4888b3aa.jpg)


Yield To Worst Ytw Definition
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Current_Yield_vs_Yield_to_Maturity_Nov_2020-02-10d2adc981ea475eb2165a5ec13082ed.jpg)


Current Yield Vs Yield To Maturity
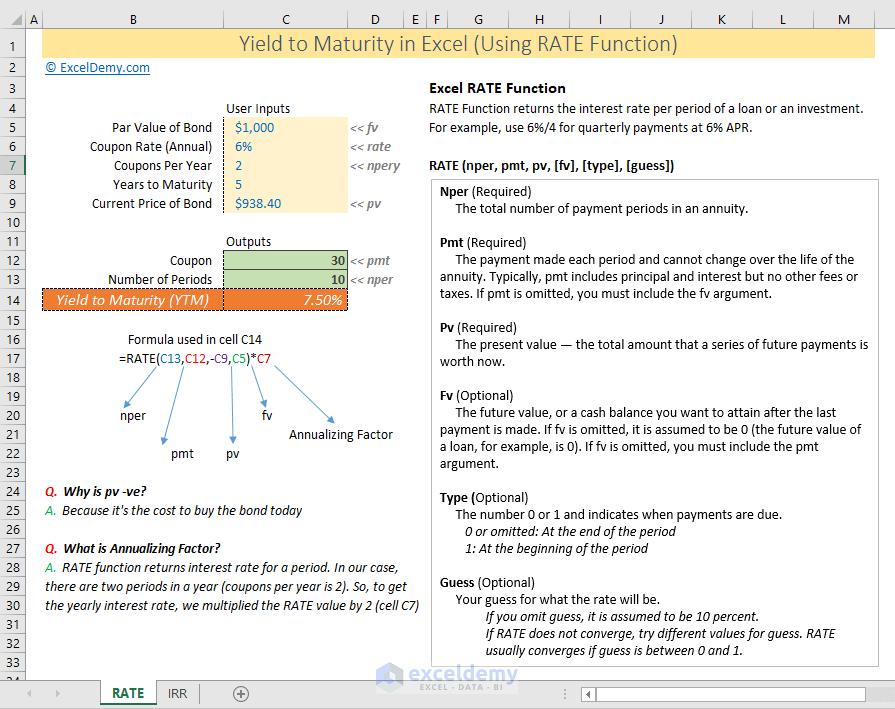


How To Calculate Yield To Maturity In Excel With Template Exceldemy
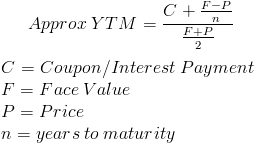


Yield To Maturity Approximate Formula With Calculator



The Complete Set Of Explicit Yield To Maturity Formulas
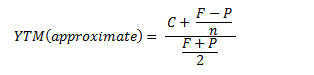


What Is The Difference Between Irr And The Yield To Maturity The Motley Fool



Bond Yield Calculator
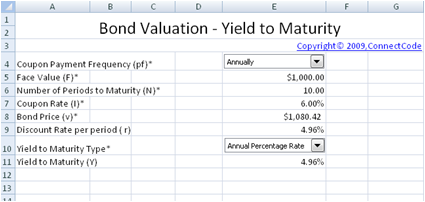


Free Bond Valuation Yield To Maturity Spreadsheet


Cost Of Debt Definition Formula Calculation Example



Finding Ytm Of A Zero Coupon Bond 6 2 1 Youtube


コメント
コメントを投稿